Understanding the Key Stages of a Typical Clinical Trial Process Flow

The process flow in a typical clinical trial is critically important for several key reasons. Firstly, it provides a structured and systematic framework that outlines the precise sequence of activities, from protocol development to data analysis. This ensures that the trial is conducted consistently and according to predefined standards.
Secondly, a well-defined process flow is essential for regulatory compliance. Clinical trials are subject to strict regulatory requirements, and a clear process flow facilitates the documentation and reporting needed to meet these standards, ensuring the trial's validity and ethical conduct. Clinical research training will help you understand the standard and help you take informed decision.
Now, we shall discuss them in detail:
Developing a clinical protocol is the first step in any clinical investigation. So, what is a Protocol? It is a document that describes how the clinical trial was carried out to ensure the safety and report of the data gathered.
After preparing the protocol report, we should go with the CRF design. The CRF is the case report and data reporting document utilized for clinical studies. Through compliance with regulatory requirements and the Protocol, the CRF gathers pertinent data in a predetermined format that enables complete and adequate processing, evaluation, and reporting. Standardization also makes it easier for data to be shared across projects and organizations. CRF designers should remember that the protocol confines what data should be piled on the CRF.
All the data must be gathered on the CRF if specified in the protocol, but data not defined on the CRF should be analyzed and should not occur on the CRF. CRF must be finalized entirely and accessible before the investigator begins registering patients into a study. Once the CRF is designed and reviewed, it should be sent to the site, and feedback must be collected from the site personnel. So, it has to be sent to the site.
The data collection process can be done with the aid of a CRF. The Case Report Form can be electronic or paper. The conventional approach involves using paper CRFs to gather data responses that are entered into the database. The investigator completes these paper CRFs following the completion guidelines.
The e-CRF method reduces the possibility of errors and speeds up the resolution of discrepancies. The CRF entries will be checked for completeness, and finalized CRFs will be collected and handed to the CDM team. Data entry operators enter CRF pages. It is recommended that after data entry is finished in the first pass, a second pass, or verification step, should be carried out by an impartial operator.
Data validation
It is the process involved in data validity testing according to protocol specifications. To verify the validity of the data, edit-check programs are designed to find inconsistencies in the entered data stored in the database. A data point is considered discrepant if it is unable to pass validation. The discrepancy could be caused by inconsistent data, missing data, range checks, or protocol deviations.
Suppose the data entered does not pass validation rules. In that case, a data query may be issued to the investigative site where the clinical trial is conducted to request clarification of the entry (Data Clarification Form).
It is possible to reconcile differences between the first and second passes so that the data entered accurately reflects the information on the CRF. The clinical data manager must be alerted if the operator cannot read the entry so those who completed the CRF can clarify it. To learn nuance of clinical data management, you can join clinical data management training and certification.
Final data validation is conducted following an appropriate quality check and assurance. The statistician consults on finalizing the SAS datasets if no discrepancies.
Database lock should have been the last step in the data management process. This is ensured by using a pre-lock checklist and verifying that all tasks have been completed.
The database is locked, and precise data is retrieved for statistical analysis as soon as locking authorization is received. SAS programmers frequently refer to this data as "raw data" because it isn't ready for analysis.
Many steps must be taken to transform raw data into analysis-ready data, also known as VAD or ADS. After creating ADSs, we generate TLFs and reports and then convert and submit CDISCs.
In conclusion, the process flow in a typical clinical trial stands as a meticulous blueprint for success. It ensures adherence to ethical, regulatory, and scientific standards while promoting efficient stakeholder coordination. By proactively managing risks and maintaining data integrity, this structured approach plays a pivotal role in developing safe and effective medical interventions, ultimately advancing healthcare and improving the well-being of patients worldwide.
Find a course provider to learn Clinical Research
Java training | J2EE training | J2EE Jboss training | Apache JMeter trainingTake the next step towards your professional goals in Clinical Research
Don't hesitate to talk with our course advisor right now
Receive a call
Contact NowMake a call
+1-732-338-7323Enroll for the next batch
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 4 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 5 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 6 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 7 2025
- Online
Related blogs on Clinical Research to learn more

CDISC SDTM: Standardizing Clinical Data for Enhanced Research Insights
Learn the importance of CDISC SDTM standards in enhancing research insights by standardizing clinical data.

Exploring the Significance of Medical History in Healthcare
Discover the crucial role of medical history in healthcare, understanding how it informs diagnosis, treatment, and patient care, and its impact on the evolution of medicine.

Key Stages of a Typical Clinical Trial Process Flow
Clinical trials follow a well-defined process flow that is essential for conducting successful and ethical clinical research.

The Indispensable Role and Importance of Industry Regulations and Standards in Clinical Trials
we have discussed key function in clinical operations, clinical research organization, key function in data management and quality assurance.

Unveiling the Clinical Research Roadmap: A Comprehensive Guide
We have discussed the purpose of Clinical research processes, and what is clinical research process.

Corona Virus (COVID-19), Symptoms, Tests and Safety Measures
Corona Virus (COVID-19), Symptoms, Tests and Safety Measures. Learn the symptoms, tests to undergo, and safety measures to be taken to prevent the virus.

List of Best Clinical Research Training in Atlanta – CRC, CRA, MSCR Studies
We have collected a list of reputed institutes to those interested in pursuing a career in clinical and/or translational research. Pick from the list to have your dream come true career in medicine.

Healthcare Sector increasing the focus in Big Data and Technology
Here the role of technology business mergers and big data firms within the healthcare frontiers comes into play. The business mergers of technology, as well as the big data firms in the healthcare sector, highlights a trend viral within the clinical

7 Ethics for Clinical Researchers
Clinical trials conducted by the researchers involve a human volunteer who is willing to be subject to adhere new findings or a medical experiment. For that, a proper consent is acquired from the volunteer before conducting the trials.

Will lowering Blood Pressure would save lives? Clinical Trials Says so…
So far, the healthcare industry had been advised that the blood pressure of a healthy adult has to be less than 140 millimeters of mercury. And any increase in blood pressure that this guideline would attract serious consequences such as heart attack
Latest blogs on technology to explore

Cyber Security in 2025: The Golden Ticket to a Future-Proof Career
Cyber security jobs are growing 35% faster than any other tech field (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024)—and the average salary is $100,000+ per year! In a world where data breaches cost businesses $4.45 million on average (IBM, 2024), cyber secu

SAP SD in 2025: Your Ticket to a High-Flying IT Career
In the fast-paced world of IT and enterprise software, SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) is the secret sauce that keeps businesses running smoothly. Whether it’s managing customer orders, pricing, shipping, or billing, SAP SD is the backbone of sales o

SAP FICO in 2025: Salary, Jobs & How to Get Certified
AP FICO professionals earn $90,000–$130,000/year in the USA and Canada—and demand is skyrocketing! If you’re eyeing a future-proof IT career, SAP FICO (Financial Accounting & Controlling) is your golden ticket. But where do you start? Sulekha IT Serv

Train Like an AI Engineer: The Smartest Career Move You’ll Make This Year!
Why AI Engineering Is the Hottest Skillset Right Now From self-driving cars to chatbots that sound eerily human, Artificial Intelligence is no longer science fiction — it’s the backbone of modern tech. And guess what? Companies across the USA and Can
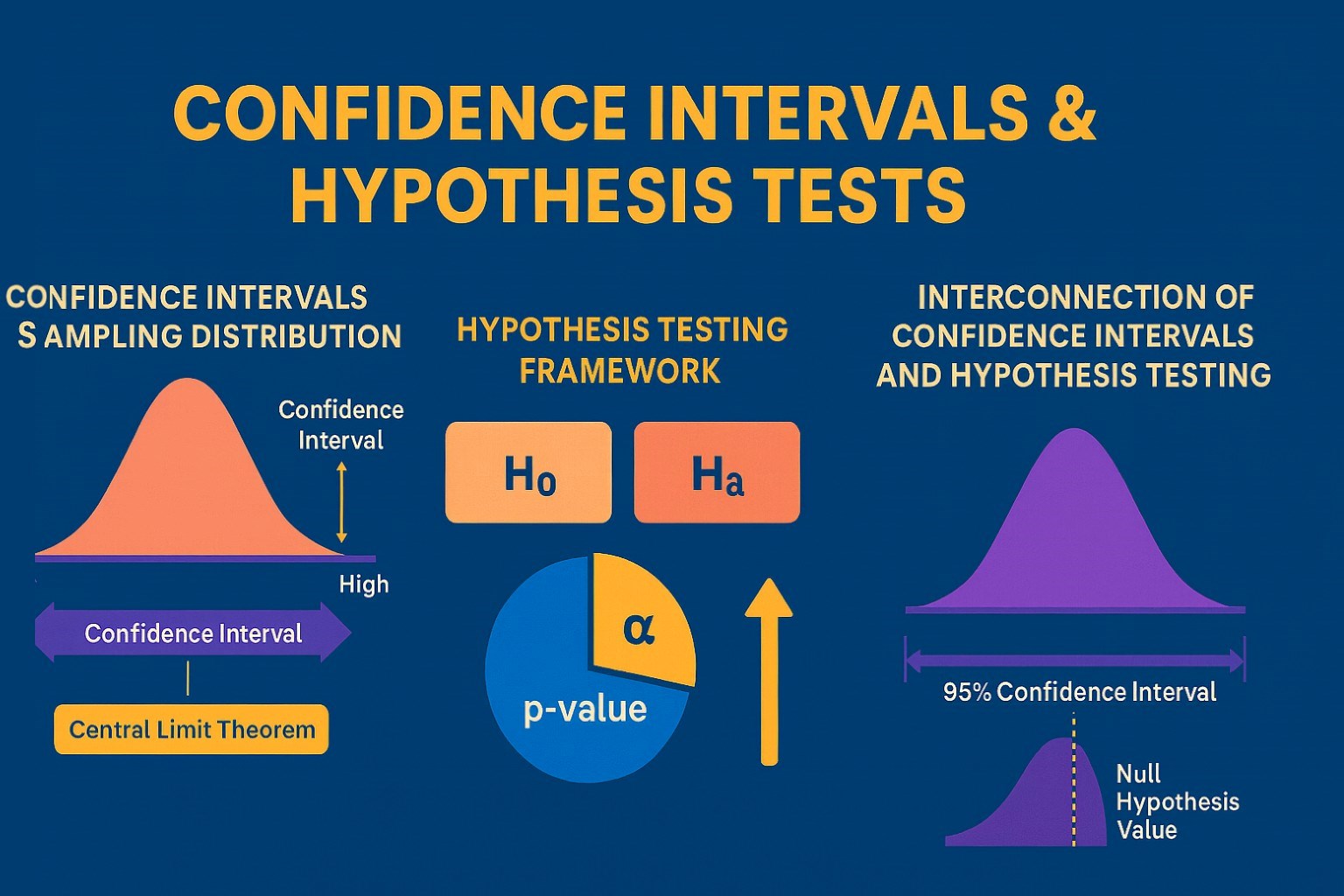
Confidence Intervals & Hypothesis Tests: The Data Science Path to Generalization
Learn how confidence intervals and hypothesis tests turn sample data into reliable population insights in data science. Understand CLT, p-values, and significance to generalize results, quantify uncertainty, and make evidence-based decisions.

What Is a Security Classification Guide in Cybersecurity?
A Security Classification Guide (SCG) defines how to categorize information assets by sensitivity, with clear instructions from authorized officials to ensure consistent, compliant data handling.
Artificial Intelligence – Field of Study
Explore how Artificial Intelligence blends Machine Learning, Deep Learning, NLP, and Computer Vision to build intelligent systems that learn, reason, and decide. Discover real world applications, ethics, and booming career scope as AI education deman

Understanding Artificial Intelligence: Hype, Reality, and the Road Ahead
Explore the reality of Artificial Intelligence (AI) — its impact, how it works, and its potential risks. Understand AI's benefits, challenges, and how to navigate its role in shaping industries and everyday life with expert training programs

How Much Do Healthcare Administrators Make?
Discover how much healthcare administrators make, the importance of healthcare, career opportunities, and potential job roles. Learn about salary ranges, career growth, and training programs with Sulekha to kickstart your healthcare administration jo

How to Gain the High-Income Skills Employers Are Looking For?
Discover top high-income skills like software development, data analysis, AI, and project management that employers seek. Learn key skills and growth opportunities to boost your career.