Exploring the Significance of Medical History in Healthcare

In CDISC SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model), "Medical History" refers to a specific domain used to systematically capture and structure information about a study participant's medical background, including any relevant medical conditions, prior illnesses, and pertinent medical events.
This domain is a standardized way to document a participant's health history, making it easier for researchers and regulators to analyze and interpret clinical trial data consistently. Variables within the Medical History domain may include details about medical diagnoses, start and end dates of conditions, severity, outcomes, and relationships to the investigational product or other therapies.
Concomitant Medication: CM
Concomitant medication refers to any medication or drug that a study participant in a clinical trial is taking concurrently with the investigational product being studied. These medications can include prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, supplements, or herbal remedies.
Concomitant medication recording is essential for clinical research and data collection because it enables researchers and medical professionals to evaluate possible drug interactions, side effects, and effects on study outcomes.
E.g. CMTRT: Paracetamol, CMDOS: 250, CMDOSU: mg, CMCAT: General.
Protocol Deviations: DV
Protocol deviations refer to instances in a clinical trial where procedures or actions do not align with the predetermined study protocol. These deviations can result from unintended errors, variations in participant adherence, or necessary deviations to ensure participant safety. Accurate recording and documentation of protocol deviations are essential for maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance in clinical research.
E.g., Drug XXXX administered during the study treatment period.
Clinical Events: CE
Clinical events in clinical research refer to significant health-related incidents or occurrences that study participants encounter during a clinical trial. Adverse events, serious adverse events, and other medically relevant incidents such as hospitalizations or deaths are examples of such events. Proper clinical event documentation and reporting are critical for monitoring participant safety and assessing the impact of investigational treatments. This event could be pre-specified on CRF.
E.g. Rash, Nausea
ECG Results: EG
ECG (Electrocardiogram) results refer to the graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart obtained through an ECG test. These results display the heart's rhythm, rate, and any potential abnormalities in the heart's electrical conduction system.
EGN- RIND: can be added to indicate where a result falls concerning the reference range defined by EGORNRLO( EG Original Normal low) and EGORNRHI. The Qualifiers: --MODIFY, --BODSYS, --SPEC is not used. e.g., EGTEST: Ventricular Rate, EGPOS: Supine, EGORRES: Abnormal.
Laboratory Test Results:
Laboratory test results are numerical or qualitative data from medical tests conducted on biological samples such as blood, urine, or tissue. These results provide essential information about a patient's health, including measures of various biomarkers, organ function, and specific conditions or diseases.
For lab tests that do not have continuous numeric results, LBSTNRC is populated. E.g. LBTEST: Glucose, LBCAT: Urine, LBORRESU: mg/dL
Physical Examination: PE
A physical examination is a methodical evaluation of an individual's general health and physiological processes carried out by a medical professional. A medical practitioner examines a patient's vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, etc.), overall appearance, body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, etc.), and any physical signs or symptoms during a physical examination.
E.g., PETESTCD: Head, PELOC: Face, PESTRESC: Normal.
Questionnaires: QS
A numerical scoring system is applied to question responses to analyze the questionnaires. Subject-reported results and validated or non-validated questionnaires are examples of questionnaire data, though they are not the only ones. When submitting a set of questions grouped on the CRF for the convenience of data capture, the QS domain is not intended for use.
E.g., QSTEST: Healthy as anybody, QSSCAT: General Health, QSORRES: True Subject Characteristics: SC
Subject Characteristics refer to information that has yet to be gathered from other subject-related domains.
Examples: subject initials, eye color, childbearing status, etc.
Based on the general observation class, the subject characteristics structure expands the demographic data. SC includes information that is either not expected to change during the trial or whose change is not significant once it has been gathered.
E.g., SCTEST: Eye Color, SCORRES: Brown, SCTESTCD: EYECD
Vital Signs: VS
Measurements like blood pressure, height, weight, pulse, and body temperature are recorded by CRF, along with deduced information like body mass index.
The allowed variable VSLOINC may be used when the LOINC dictionary is utilized for vital sign assessments. The reference range that VSORNRLO and VSORNRHI define can be used to determine a result's location using VSNRIND.
E.g., VSTEST: Systolic Blood Pressure, VSPOS: Sitting, VSORRES: 154, VSSORRESU: mmHg.
How are the domains captured on a case report form?
The corresponding variables for each domain are annotated on the Case Report form; for example, the subject's initials would be annotated as SUBJID. Annotation of the Study Number as STUDYID will be created. A USUBJID could be annotated by combining the STUDYID and the SUBJID.
SDTM Dates: Represented in ISO 8601 format as a complete date/time, a partial date/time, or an incomplete date/time i.e., YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss
E.g., December 15, 2003 13:15:17 ? 2003-12-15T13:15:17
In conclusion, understanding and effectively utilizing a patient's medical history is of paramount importance in the field of healthcare. This comprehensive overview has highlighted the multifaceted significance of medical history, emphasizing its role in diagnosis, treatment planning, risk assessment, and patient-centered care. By harnessing the wealth of information in medical histories, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
As we continue to advance in healthcare technology and data integration, it becomes even more crucial to prioritize the accurate and thorough documentation and utilization of medical histories. Embracing the power of medical history can ultimately lead to a brighter and healthier future for both patients and healthcare systems alike.
Find a course provider to learn Clinical Research
Java training | J2EE training | J2EE Jboss training | Apache JMeter trainingTake the next step towards your professional goals in Clinical Research
Don't hesitate to talk with our course advisor right now
Receive a call
Contact NowMake a call
+1-732-338-7323Enroll for the next batch
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 4 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 5 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 6 2025
- Online
Clinical Research Training Course Program
- Nov 7 2025
- Online
Related blogs on Clinical Research to learn more

CDISC SDTM: Standardizing Clinical Data for Enhanced Research Insights
Learn the importance of CDISC SDTM standards in enhancing research insights by standardizing clinical data.

Key Stages of a Typical Clinical Trial Process Flow
Clinical trials follow a well-defined process flow that is essential for conducting successful and ethical clinical research.

Understanding the Key Stages of a Typical Clinical Trial Process Flow
Discover the critical steps involved in each stage, ensuring a smooth and successful clinical trial process flow.

The Indispensable Role and Importance of Industry Regulations and Standards in Clinical Trials
we have discussed key function in clinical operations, clinical research organization, key function in data management and quality assurance.

Unveiling the Clinical Research Roadmap: A Comprehensive Guide
We have discussed the purpose of Clinical research processes, and what is clinical research process.

Corona Virus (COVID-19), Symptoms, Tests and Safety Measures
Corona Virus (COVID-19), Symptoms, Tests and Safety Measures. Learn the symptoms, tests to undergo, and safety measures to be taken to prevent the virus.

List of Best Clinical Research Training in Atlanta – CRC, CRA, MSCR Studies
We have collected a list of reputed institutes to those interested in pursuing a career in clinical and/or translational research. Pick from the list to have your dream come true career in medicine.

Healthcare Sector increasing the focus in Big Data and Technology
Here the role of technology business mergers and big data firms within the healthcare frontiers comes into play. The business mergers of technology, as well as the big data firms in the healthcare sector, highlights a trend viral within the clinical

7 Ethics for Clinical Researchers
Clinical trials conducted by the researchers involve a human volunteer who is willing to be subject to adhere new findings or a medical experiment. For that, a proper consent is acquired from the volunteer before conducting the trials.

Will lowering Blood Pressure would save lives? Clinical Trials Says so…
So far, the healthcare industry had been advised that the blood pressure of a healthy adult has to be less than 140 millimeters of mercury. And any increase in blood pressure that this guideline would attract serious consequences such as heart attack
Latest blogs on technology to explore

Cyber Security in 2025: The Golden Ticket to a Future-Proof Career
Cyber security jobs are growing 35% faster than any other tech field (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024)—and the average salary is $100,000+ per year! In a world where data breaches cost businesses $4.45 million on average (IBM, 2024), cyber secu

SAP SD in 2025: Your Ticket to a High-Flying IT Career
In the fast-paced world of IT and enterprise software, SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) is the secret sauce that keeps businesses running smoothly. Whether it’s managing customer orders, pricing, shipping, or billing, SAP SD is the backbone of sales o

SAP FICO in 2025: Salary, Jobs & How to Get Certified
AP FICO professionals earn $90,000–$130,000/year in the USA and Canada—and demand is skyrocketing! If you’re eyeing a future-proof IT career, SAP FICO (Financial Accounting & Controlling) is your golden ticket. But where do you start? Sulekha IT Serv

Train Like an AI Engineer: The Smartest Career Move You’ll Make This Year!
Why AI Engineering Is the Hottest Skillset Right Now From self-driving cars to chatbots that sound eerily human, Artificial Intelligence is no longer science fiction — it’s the backbone of modern tech. And guess what? Companies across the USA and Can
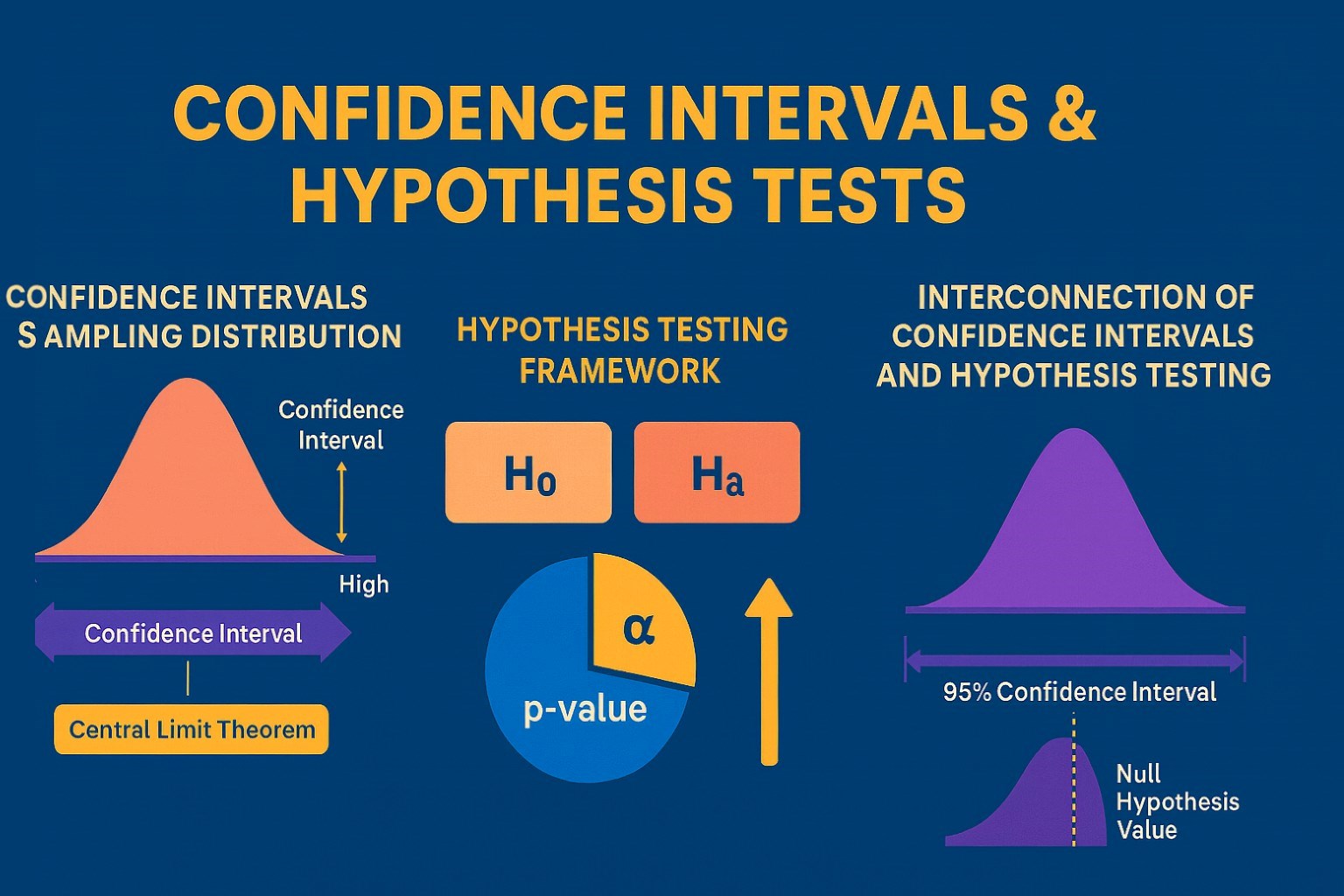
Confidence Intervals & Hypothesis Tests: The Data Science Path to Generalization
Learn how confidence intervals and hypothesis tests turn sample data into reliable population insights in data science. Understand CLT, p-values, and significance to generalize results, quantify uncertainty, and make evidence-based decisions.

What Is a Security Classification Guide in Cybersecurity?
A Security Classification Guide (SCG) defines how to categorize information assets by sensitivity, with clear instructions from authorized officials to ensure consistent, compliant data handling.
Artificial Intelligence – Field of Study
Explore how Artificial Intelligence blends Machine Learning, Deep Learning, NLP, and Computer Vision to build intelligent systems that learn, reason, and decide. Discover real world applications, ethics, and booming career scope as AI education deman

Understanding Artificial Intelligence: Hype, Reality, and the Road Ahead
Explore the reality of Artificial Intelligence (AI) — its impact, how it works, and its potential risks. Understand AI's benefits, challenges, and how to navigate its role in shaping industries and everyday life with expert training programs

How Much Do Healthcare Administrators Make?
Discover how much healthcare administrators make, the importance of healthcare, career opportunities, and potential job roles. Learn about salary ranges, career growth, and training programs with Sulekha to kickstart your healthcare administration jo

How to Gain the High-Income Skills Employers Are Looking For?
Discover top high-income skills like software development, data analysis, AI, and project management that employers seek. Learn key skills and growth opportunities to boost your career.